Computing Power Spectra¶
With an initialized model, we can compute the power spectrum either
as a function of \(k\) and \(\mu\), \(P(k,\mu)\), or compute
the multipoles of the power spectrum, \(P_\ell(k)\). This
is accomplished either by calling the GalaxySpectrum.power()
or GalaxySpectrum.poles() functions.
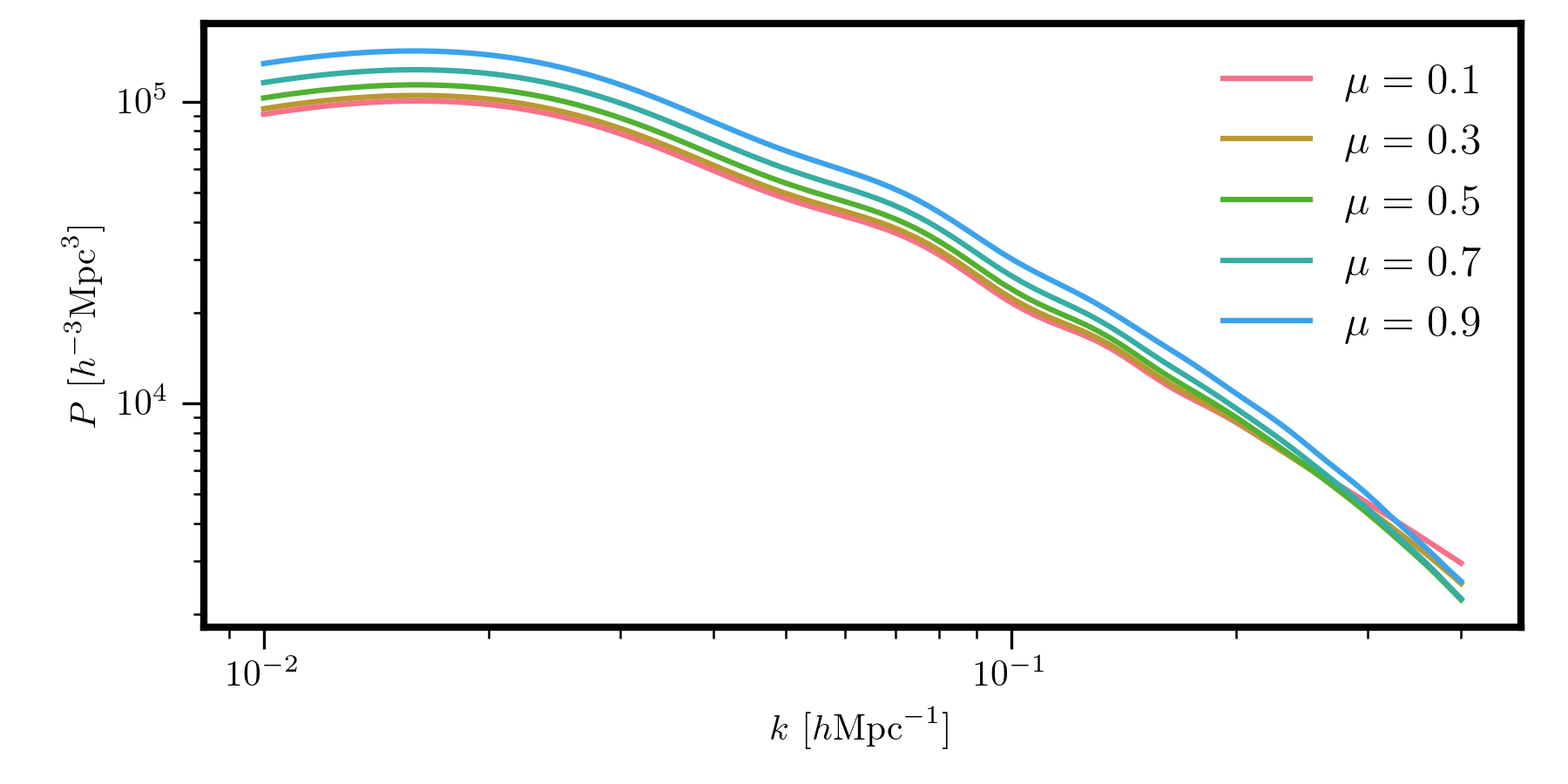
For example, to compute \(P(k,\mu)\) for 5 \(\mu\) bins:
k = numpy.logspace(-2, numpy.log10(0.4), 100)
# this is mu = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9
mu = numpy.arange(0.1, 1.0, 0.2)
Pkmu = model.power(k, mu) # shape is (100,5)
for i, imu in enumerate(mu):
plt.loglog(k, Pkmu[:,i], label=r"$\mu = %.1f$" %imu)
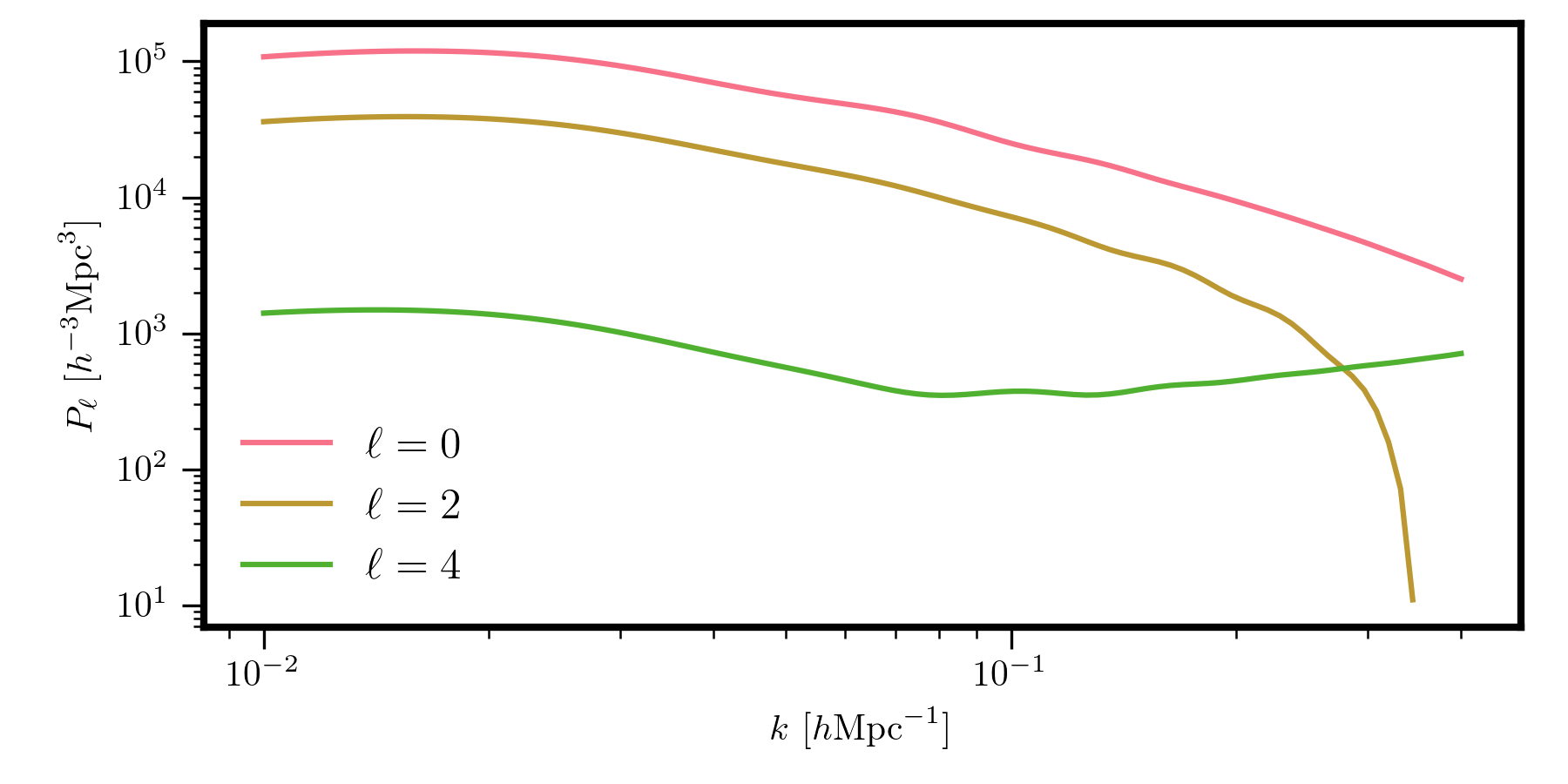
And, for example, the monopole, quadrupole, and hexadecapole (\(\ell=0,2,4\)) can be computed as
ells = [0, 2, 4]
Pell = model.poles(k, ells) # list of 3 (100,) arrays
for i, ell in enumerate(ells):
plt.loglog(k, Pell[i], label=r"$\ell = %d$" %ell)