Overview¶
The pyRSD.rsd.hzpt module provides functionality for computing various
power spectrum and correlation function quantities using Halo Zel’dovich
Perturbation Theory (HZPT). See Seljak and Vlah 2015
for an introduction to HZPT.
The Fourier space quantities can be computed from the following classes:
| Name | Quantity |
|---|---|
HaloZeldovichP00 |
The dark matter auto power spectrum |
HaloZeldovichP01 |
The dark matter density - radial momentum cross correlation |
HaloZeldovichP11 |
The \(mu^4\) contribution to the radial momentum auto spectrum |
HaloZeldovichPhm |
The halo - dark matter cross power |
And the configuration space quantities can be computed from the following classes:
| Name | Quantity |
|---|---|
HaloZeldovichCF00 |
The dark matter auto correlation function |
HaloZeldovichCFhm |
The halo - dark matter cross correlation function |
Initialization¶
An HZPT instance can be initialized by specifying a cosmology via a
pyRSD.rsd.cosmology.Cosmology object and a redshift z.
Note
The objects should be initialized at a specific redshift by passing
the z parameter. Once created, the sigma8_z attribute can be adjusted
to compute the clustering quantity at different redshifts.
Functions¶
The HZPT class objects are callable objects; they return either the HZPT power
spectrum or correlation function at the specified wavenumber k or
separation r. The zeldovich function returns the Zel’dovich term and
the broadband function returns the Padé correction term.
Examples¶
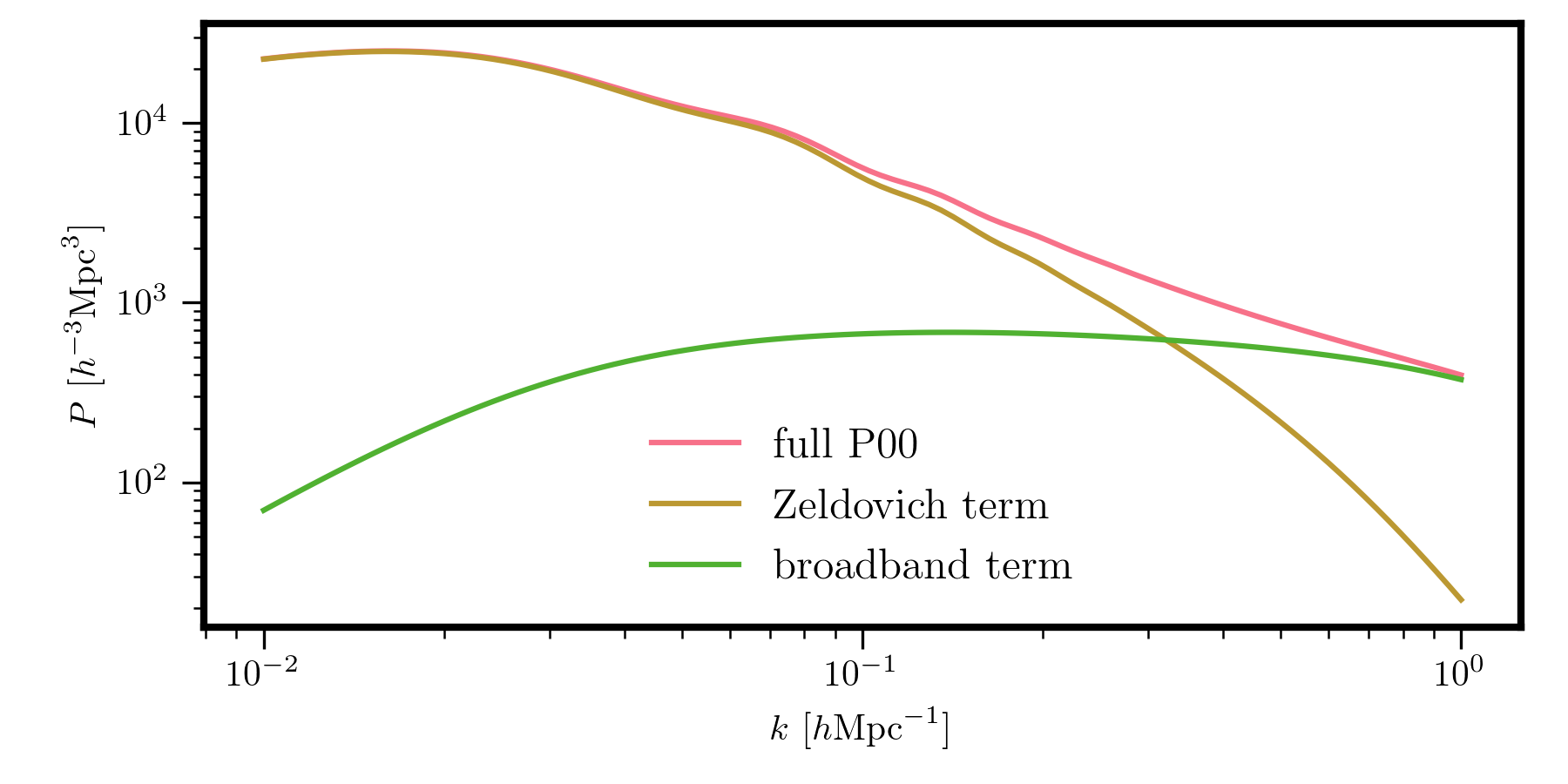
For example, to compute the dark matter auto spectrum for the Planck 2015 cosmology,
from pyRSD.rsd.cosmology import Planck15
from pyRSD.rsd.hzpt import HaloZeldovichP00
# power spectrum at z = 0
P00 = HaloZeldovichP00(Planck15, z=0.)
# compute the full power and each term
k = np.logspace(-2, 0, 100)
Pk = P00(k)
Pzel = P00.zeldovich(k)
Pbb = P00.broadband(k)
# and plot
plt.loglog(k, Pk, label='full P00')
plt.loglog(k, Pzel, label='Zeldovich term')
plt.loglog(k, Pbb, label='broadband term')
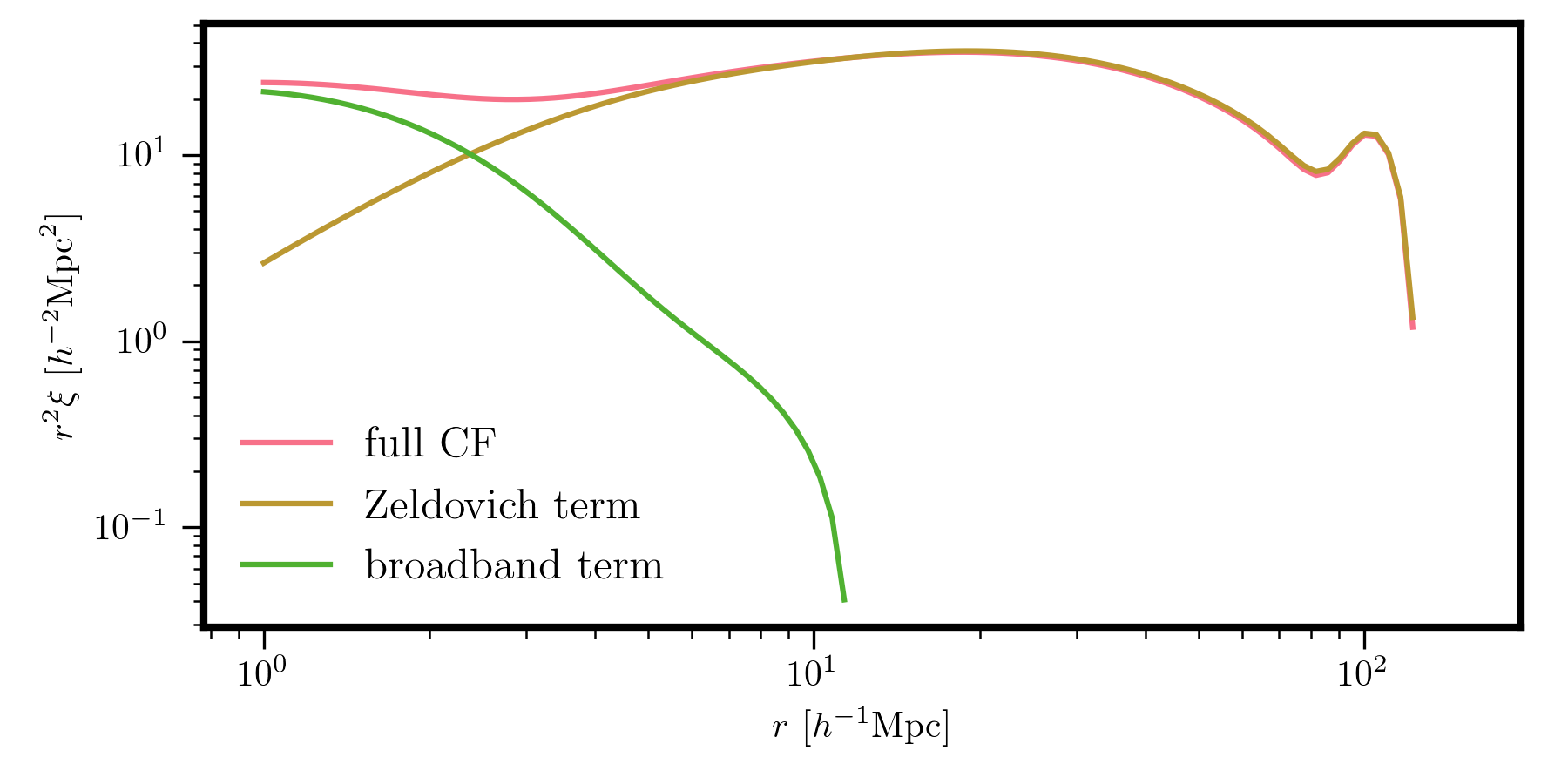
Similary, the dark matter correlation function and the various terms can be computed as:
from pyRSD.rsd.hzpt import HaloZeldovichCF00
# correlation function at z = 0
CF = HaloZeldovichCF00(Planck15, z=0.)
# compute the full correlation and each term
r = np.logspace(0, np.log10(150), 100)
xi = CF(r)
xi_zel = CF.zeldovich(r)
xi_bb = CF.broadband(r)
# and plot
plt.loglog(r, r**2 * xi, label='full CF')
plt.loglog(r, r**2 * xi_zel, label='Zeldovich term')
plt.loglog(r, r**2 * xi_bb, label='broadband term')